
1.Introduction to FPC
FPC: English spelling Flexible Printed Circuit, which means flexible printed circuit board, referred to as soft board. It is made by using photo-imaging pattern transfer and etching process on the surface of a flexible substrate to make conductor circuit patterns. The surface and inner layers of double-sided and multi-layer circuit boards are electrically connected to the inner and outer layers through metallized holes. , The surface of the circuit pattern is protected and insulated by PI and adhesive layer.
It is mainly divided into single panel, hollow panel, double panel, multi-layer panel and rigid-flex panel.
PCB: English spelling Printed Circuit Board, which means steel printed circuit board, referred to as hard board.
2.Development Trend
The FPC industry first emerged in Japan around 2002. The FPC industry outside Japan began to sprout in 2003, expanded rapidly in 2005, and declined in 2006. The FPC industry fell to the bottom in mid-2007, and began to recover in 2008.
In 2005, the low threshold and high profit of the soft board industry attracted a large number of enterprises to enter.
In 2006, competition has become increasingly fierce, and the phenomenon of oversupply is very serious. In order to survive, many companies have to drop prices again and again, and even operate at a loss. At the same time, downstream customers of the FPC industry, such as large EMS manufacturers, have added FPC departments and no longer outsourced FPC business, which has made the FPC industry even worse.
2007 was a precarious year for the FPC industry. The first is the sharp decline in profits. The major FPC manufacturer M-FLEX’s net profit in fiscal year 2007 was only US$3 million, while the net profit in fiscal year 2006 reached US$40.4 million, a 93% drop in net profit. Hong Kong-listed Giti Technology posted a loss of $29.8 million in fiscal 2007, compared with a profit of $12.4 million in fiscal 2006. The second is the decline in sales. Jialianyi, the largest soft board factory in Taiwan, had sales of NT$7.79 billion in 2004, and then declined for three consecutive years, with sales of NT$6.541 billion in 2007.
Again, the gross profit margin declined. Jialianyi’s gross profit margin was 29% in 2004, and dropped to 12% in 2007. Young Poong, South Korea’s largest soft board company, has divested its soft board business from a listed company to prevent investors from looking too ugly. The big factories are still like this, and the small factories are directly closed down.
The large number of closures of small factories has brought opportunities to the FPCB industry, which has been recovering since the beginning of 2008. But the FPC industry is facing a new problem, which is the economic downturn. At the beginning of 2008, the global economy showed a downward trend, with soaring oil prices, subprime mortgage crisis, and skyrocketing food prices. The global economy has entered a downward channel, especially in emerging countries. The decline in demand for flexible boards stems from consumer electronics. When the economy is in the downward channel, the first thing to be hit is the demand for these non-rigid consumer electronic products: including mobile phones, notebook computers, flat-panel TVs, LCD monitors, digital cameras, DVs and other products.
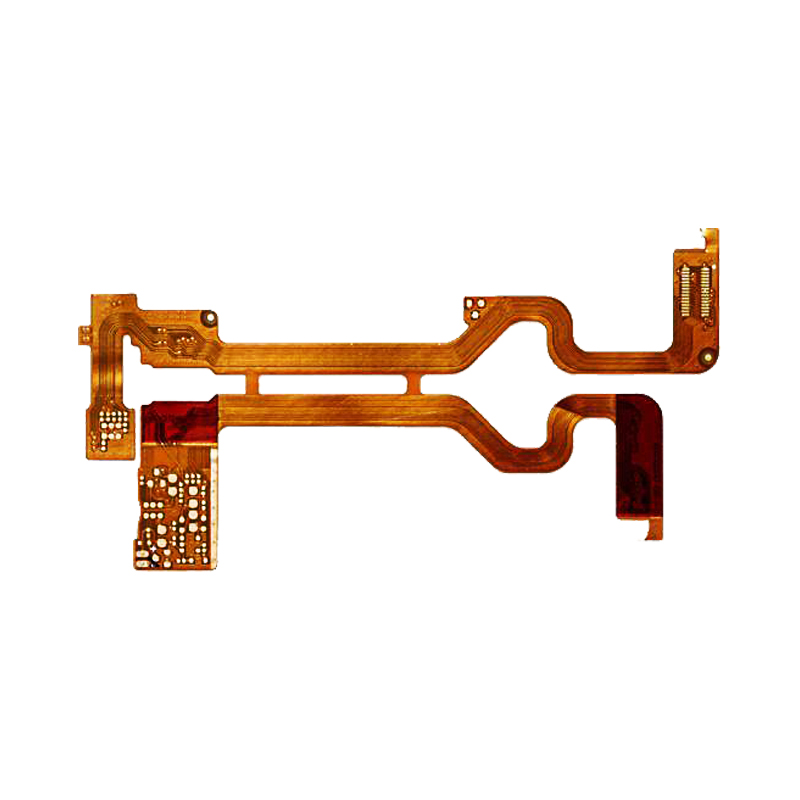
3.Features of flexible circuit boards
- Short: Short assembly time
All lines are configured, eliminating the need to connect redundant cables;
- Small: smaller than PCB (hard board)
It can effectively reduce the volume of the product and increase the convenience of carrying;
- Light: lighter than PCB (hard board)
The weight of the final product can be reduced;
- Thin: thinner than PCB (hard board)
It can improve the softness and strengthen the assembly of three-dimensional space in a limited space.
Advantages of flexible circuit boards
A flexible printed circuit board is a printed circuit made of a flexible insulating substrate, which has many advantages that rigid printed circuit boards do not have:
- It can be bent, wound, and folded freely, and can be arbitrarily arranged according to the spatial layout requirements, and can be moved and stretched arbitrarily in three-dimensional space, so as to achieve the integration of component assembly and wire connection;
- The use of FPC can greatly reduce the volume and weight of electronic products, which is suitable for the development of electronic products in the direction of high density, miniaturization and high reliability. Therefore, FPC has been widely used in aerospace, military, mobile communications, laptop computers, computer peripherals, PDA, digital cameras and other fields or products;
- FPC also has the advantages of good heat dissipation and solderability, easy assembly and connection, and low comprehensive cost. The design of soft and hard combination also makes up for the slight deficiency of the flexible substrate in the component carrying capacity to a certain extent.
Disadvantages of flexible circuit boards
- High one-time initial cost: Since flexible PCBs are designed and manufactured for special applications, the initial circuit design, wiring and photographic negatives are expensive. Unless there is a special need to apply a flexible PCB, it is usually best not to use it in a small amount of application;
- It is difficult to change and repair the flexible PCB: once the flexible PCB is made, it must be changed from the base map or the compiled light drawing program, so it is not easy to change. The surface is covered with a layer of protective film, which must be removed before repairing and restored after repairing, which is a relatively difficult work;
- The size is limited: flexible PCBs are usually manufactured by batch method when they are not yet common, so they cannot be made very long and wide due to the limitation of the size of production equipment;
- Improper operation is easy to damage: improper operation of the installation and connection personnel can easily cause damage to the flexible circuit, and its soldering and rework need to be operated by trained personnel.

4.FPC main raw materials
The main raw materials are:
(1) Base material, (2) Cover film, (3) Reinforcement, (4) Other auxiliary materials.
1. Substrate
1-1 Adhesive substrate
The adhesive substrate is mainly composed of three parts: copper foil, adhesive, and PI. There are two types of single-sided substrates and double-sided substrates. The material with only one copper foil is a single-sided substrate, and the material with two copper foils is Double-sided substrate.
1-2 Adhesive-free substrate
The adhesive-free substrate is a substrate without an adhesive layer. Compared with the ordinary adhesive substrate, the middle adhesive layer is missing, and it is only composed of copper foil and PI, which is thinner than the adhesive substrate. , better dimensional stability, higher heat resistance, higher bending resistance, better chemical resistance and other advantages, have now been widely used.
Copper foil: At present, the thickness of commonly used copper foil has the following specifications, 1OZ, 1/2OZ, 1/3OZ, and now a thinner copper foil with a thickness of 1/4OZ is introduced, but this material is currently used in China, and it is making ultra-fine roads. (Line width and line spacing are 0.05MM and below) products. As customer requirements become higher and higher, materials of this specification will be widely used in the future.
2. Cover film
It is mainly composed of three parts: release paper, glue, and PI. In the end, only glue and PI remain on the product. The release paper will be torn off during the production process and will not be used (it acts as a protective glue with foreign bodies on it). ).
3. Reinforcement
It is a specific material for FPC and is used in a specific part of the product to increase the support strength and make up for the “soft” feature of FPC.
The commonly used reinforcing materials are as follows:
1) FR4 reinforcement: the main components are glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin glue, which is the same as the FR4 material used in PCB;
2) Steel sheet reinforcement: the composition is steel, which has strong hardness and support strength;
3) PI reinforcement: the same as the cover film, it consists of PI and adhesive release paper, but the PI layer is thicker, and can be produced in proportions from 2MIL to 9MIL.
4. Other auxiliary materials
1) Pure glue: This adhesive film is a heat-curing acrylic adhesive film composed of protective paper/release film and a layer of glue, mainly used for layered boards, flexible and rigid boards, and FR -4/Steel sheet reinforcement board, play a role in bonding.
2) Electromagnetic protective film: paste it on the board surface for shielding.
3) Pure copper foil: only composed of copper foil, mainly used for hollow plate production.

5.Types of FPC
FPC types have the following 6 distinctions:
A. Single panel: only one side has lines.
B. Double-sided: There are lines on both sides.
C. Hollow board: also known as window plate (finger cover layer open).
D. Layered board: lines on both sides (separate).
E. Multilayer board: more than two layers of lines.
F. Rigid-flex board: a product that combines soft board and hard board.
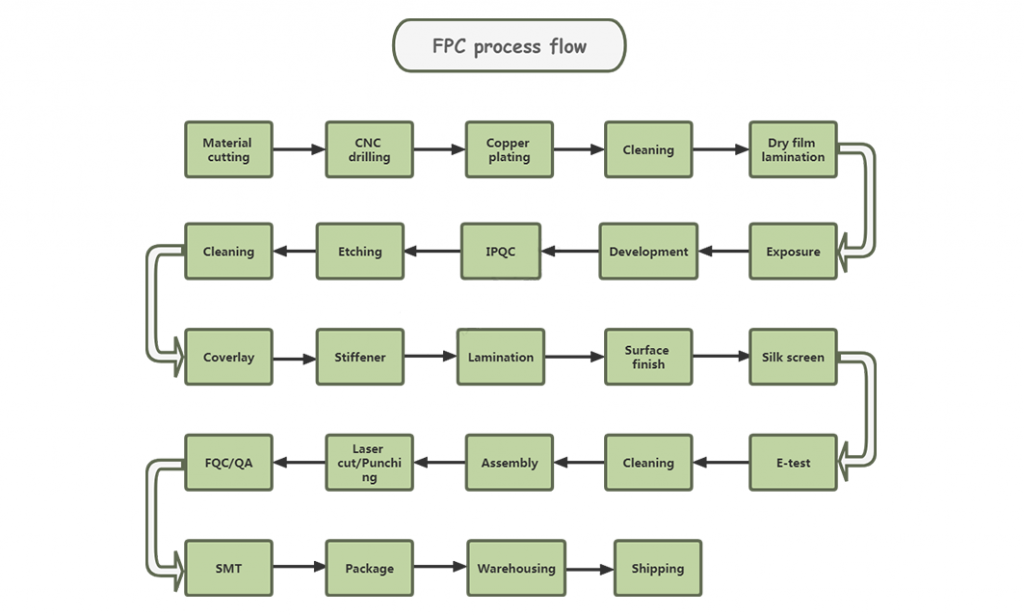
6.FPC process flow
If you have any PCB demands, please feel free to contact us.
Email:[email protected]
Skype:[email protected]
Telephone number:+86 133 9241 2348
Whatsapp: +86 133 9241 2348