1.Significantly improve product quality and reliability
When the Flex-Rigid PCB is applied to the car, the connectors and solder joints can be reduced, which can reduce the potential risk of electrical failure. The performance and reliability of automotive electronic control systems will be proportional to the reduction in connectors and welded joints.
2.Reduced costs due to reduced manufacturing steps
With the application of Flex-Rigid PCBs, the soldering of ribbon cables and assembled connectors will be cut, thereby reducing costs. After all, the implementation of all manufacturing processes is expensive.
3.Maintenance simplified and eliminated
The Flex-Rigid PCB used for automobiles is composed of two or more pieces of rigid material and one or more pieces of flexible material, and the rigid parts are connected to each other through the application of flexible materials. Each Flex-Rigid circuit can be accurately packaged in a smaller package, which can eliminate a lot of management and maintenance.
4.Designer and assembly free improvement
Flex-Rigid circuit designers are only responsible for rigid circuit board layout. For the flexible part, they only need to guide the connection, and can be freely fixed, sling or piling, which greatly simplifies the design and assembly.
So far, two types of Flex-Rigid PCBs are currently on the market:
a. Semi-flexible PCB. The flexible part of the semi-flex PCB is made of thin FR-4 material, which is especially suitable for assembly, requiring only a few flexibility. In addition, the semi-flexible PCB leads to low cost.
b. Multi-flex PCB. The multi-layer flexible PCB is made of polyimide (PI) material, which can meet applications requiring dynamic flexibility. Since the PI layer can be extended to the inner rigid part of the Flex-Rigid PCB, the multi-flex circuit board is more suitable for applications that require gradual dynamic flexibility.
Multi-flex PCB
The flexible part of the Flex-Rigid PCB is made of flexible PI copper foil material, which belongs to the multi-flex PCB category. Multi-flex PCB is a kind of traditional Flex-Rigid PCB, which has been used for more than 30 years. The multi-flex PCB has a hybrid structure laminated by rigid substrate materials and flexible substrate materials, and the interconnection between the electrical conductors is achieved through plated through holes that will pass through the Flex-Rigid materials. Figure 1 below shows the structure of a double-layer flexible circuit board.
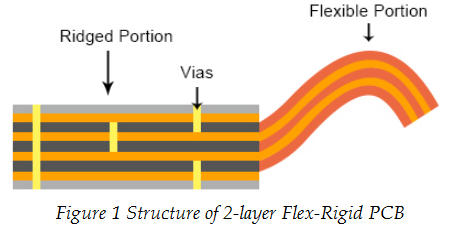
According to Figure 1, it can be concluded that the flexible substrate material depends on the common PI copper foil material, which is not only laid on the flexible part, but also covers all rigid parts. However, laying some PI copper foil structures in selective sections is equivalent. Once flexible PI copper foil is used for selective parts, manufacturing complexity will increase, and this method is generally rarely used.
When it comes to multilayer flexible PCBs, because of the relatively high CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion) along the Z-axis bonding direction, the adhesive may cause mechanical damage to the plated through holes during stress testing or thermal shock testing. Therefore, when automotive PCBs require higher thermal reliability, it is necessary to avoid the use of flexible substrate materials and a cover layer covering the rigid part, because plated vias can usually be used for the rigid part.
In addition, because FR4 prepreg is also a substrate with high CTE, the reliability of ordinary FR4 adhesives and non-flowing prepregs must be considered. The Tg of ordinary FR4 non-flowing prepreg is 105°C, which is about 30°C lower than traditional FR4 prepreg.
In addition to materials other than FR4 materials used as rigid substrates, almost any type of rigid material is suitable for multi-flex PCBs, including high Tg materials, halogen-free materials and even high-frequency materials.
Most flexible materials used for Flex-Rigid PCB use PI with adhesive or PI without adhesive, the effect is better. However, PEN and PET materials can also be used for simple and asymmetric Flex-Rigid circuit board structures. LCP (liquid crystal polymer) material can be regarded as the best flexible material without adhesive, with high reliability design and high-speed signal transmission design. It is recommended to bake them before application to eliminate the humidity caused by the high humidity absorption of PI. However, the multi-flex PCB using LCP as the substrate material does not need to be baked.
As far as Flex-Rigid PCBs are concerned, multiple flexible circuits can provide some flexible layers that can be used at the same time. Since the complex interconnection of the circuit is an integrated design, it can be repeatedly manufactured, which is more advantageous than the connection of cables and wires. Therefore, the characteristic impedance control signal transmission line design can be realized to replace the coaxial cable.
Semi-flexible PCB
Semi-flex PCB cannot achieve continuous flexibility. In fact, in many applications, the flexible part of a Flex-Rigid PCB only has some flexibility, such as during assembly, rework, and maintenance. Therefore, an expensive flexible material such as PI is not necessary for this application and it is sufficient to use a bendable material. In addition, costs can be reduced. The semi-flexible PCB can use traditional substrate materials for multilayer lamination, thereby avoiding the lamination of different materials together and minimizing internal thermal stress. In order to obtain a flexible material, the best method is to make the traditional FR4 substrate material bend enough. Of course, another method is to selectively reduce the thickness of the flexible portion.
Semi-flexible PCBs are PCBs manufactured by adhering to the same manufacturing technology as traditional double-sided PCBs and multilayers. The thinning of the flexible part can be done by milling. In addition, semi-flexible PCBs are manufactured by adhering to similar manufacturing techniques to traditional PCBs, except for the addition of flexible manufacturing.