1. The core of the high-density interconnection board (HDI) is in the via
The circuit processing of multi-layer PCB is no different from single-layer and double-layer. The biggest difference lies in the process of vias.
The lines are all etched, and the vias are all drilled and then plated with copper. Everyone who does hardware development understands these, so I won’t go into details.
Multilayer circuit boards usually include through-hole boards, first-level boards, second-level boards, and second-level stacked-hole boards. Higher-end boards, such as third-order boards and arbitrary-layer interconnect boards, are usually used very little and are expensive, so I won’t discuss them first.
In general, 8-bit single-chip products use 2-layer through-hole boards; 32-bit single-chip-level smart hardware uses 4-layer-6-layer through-hole boards; Linux and Android-level smart hardware uses 6-layer through-hole to 8-level HDI board: Compact products such as smart phones generally use 8-layer first-order to 10-layer 2-layer circuit boards.

2. The most common through holes
There is only one type of via, from the first layer to the last layer. Regardless of whether it is an external circuit or an internal circuit, the holes are punched through, which are called through-hole boards.
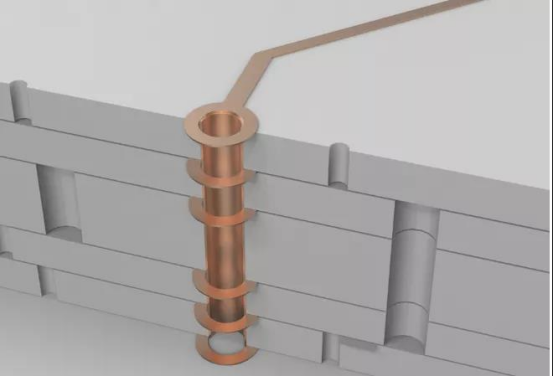
Through-hole boards and the number of layers do not matter. Everyone usually uses two-layer through-hole boards, but many switches and military circuit boards do 20-layer through-hole boards.
Use a drill to drill through the circuit board, and then plate the hole with copper to form a via.
It should be noted here that the inner diameter of the through hole is usually 0.2mm, 0.25mm and 0.3mm, but generally 0.2mm is much more expensive than 0.3mm. Because the drill bit is too thin and easy to break, the drill is slower. The time spent and the cost of the drill bit are reflected in the increase in the price of the circuit board.
3. Laser hole of high density board (HDI board)
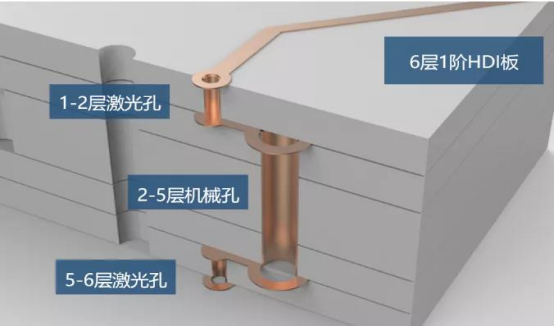
This picture is a laminated structure picture of a 6-layer 1-stage HDI board. Both layers on the surface are laser holes with an inner diameter of 0.1mm. The inner layer is a mechanical hole, which is equivalent to a 4-layer through-hole board, and the outer layer is covered with 2 layers.
The laser can only penetrate glass fiber sheets, not metal copper. Therefore, the outer surface punching will not affect other internal circuits.
After the laser drills the hole, go to copper plating, and the laser via is formed.
4.2-level HDI board with two layers of laser holes
This picture is a 6-layer, 2-step HDI board with misaligned holes. Usually, people use 6 floors and 2 levels few, and most of them start with 8 floors and 2 levels. There are more layers here, the same as 6 layers.
The so-called 2nd order means that there are 2 layers of laser holes.
The so-called wrong hole means that the two layers of laser holes are staggered.
Why should it be staggered? Because the copper plating is not full, the inside of the hole is empty, so you can’t drill holes directly on it, you have to stagger a certain distance, and then make a layer of empty.
6 layers of second order = 4 layers of 1 order plus 2 layers outside.
8 layers of second order = 6 layers of 1 order plus 2 layers outside.
5. Stacked orifice plate, the process is more complicated and the price is higher
The two layers of laser holes of the staggered hole plate overlap each other. The line will be more compact.
The inner laser hole needs to be electroplated and filled, and then the outer laser hole is made. The price is more expensive than the wrong hole.
6. Super expensive any layer interconnection board with multilayer laser stacking holes
That is, each layer is a laser hole, and each layer can be connected together. You can route the cables as you want, or punch as you want.
Any PCB need production please Contact us freely! BETON PCBs Factory email:[email protected]